What is Methyl Acetate?
Methyl acetate (also known as methyl ethanoate, acetic acid methyl ester, MeOAc, Tereton, Devoton) is a carboxylate ester with a molecular formula of C3H6O2. It is a clear, colourless liquid that has a typical ester odour similar to glues and nail polish removers. It is very flammable with a flashpoint of -10° C and a flammability rating of 3. Methyl acetate is commonly used in low toxicity solvents such as glues, nail polish removers.
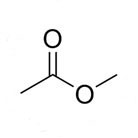
It is highly miscible with all common organic solvents (alcohols, ketones, glycols, esters) but has only slight miscibility in water, but becomes more soluble in water with elevated temperatures. It is commonly found in fruits such as apples, grapes and bananas.
Methyl ethanoate technical properties
Chemical and physical properties of methyl acetate:
Molecular Formula: C3H6O2 / CH3COOCH3
Synonyms: methyl ethanoate, acetic acid methyl ester, MeOAc, tereton, devoton, methyl ester of acetic acid, methylacetate
Cas Number: 79-20-9
Molecular Mass: 74.079 g·mol−1
Exact Mass: 74.036779 g/mol
Flashpoint: 14 °F / -10 °C
Boiling Point: 134.4 °F at 760 mm Hg / 56.8 °C
Melting Point: -144 °F / -98.0 °C
Vapour Pressure: 170 mm Hg at 68 ° F ; 235 mm Hg at 77° F
Water Solubility: ~25% (20 °C)
Density: 0.932 g cm−3
Log P: 0.18
Methyl acetate is a carboxylate ester as it contains a carbonyl group bonded to an OR group and is produced through the esterification of acetic acid with methanol.
How is methyl acetate produced?
There are various methods of producing methyl acetate. One that is used industrially is via carbonylation. These types of reactions bring together carbon monoxide substrates. To produce methyl acetate, methanol is heated alongside acetic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid. Another method of production is the esterification of methanol and acetic acid in the presence of a strong acid. Sulfuric acid is a common catalyst also used in this reaction.
Handling, Storage & Distribution
Hazards & Toxicity
Methly acetate has a NFPA health rating of 2 and can cause temporary incapacitation or residual injury. If inhaled or ingested, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue can occur. Contact with the eyes can cause irritation. It has a flammability rating of 3 and can be ignited under most ambient temperature conditions residing from its low flash point of -10 °C. When ablaze, methyl acetate emits heavy, irritating, and toxic fumes that can travel considerable distances. These vapours are also explosive and risk bursting if able to return to the source of ignition.
Methyl acetate’s reactivity is aligned with other compounds of the ester group. In the presence of strong bases or acids such as sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid at high temperatures, it is converted back into methanol and acetic acid.
Storage & Distribution
Methyl acetate should be stored in a storage area specialised for flammable liquids, tightly enclosed in drummed containers such as isotanks made of stainless steel, aluminium or carbon steel. This area should be cool, dry and well-ventilated, out of direct sunlight, heat, open flames and away from strong acids and alkalis, nitrates and strong oxidisers.
A bulk solvent exporter would normally distribute in bulk vessels or tank trucks. For transportation purposes, methyl acetate is classed as a flammable liquid with a fire hazard rating of 2 and is a packing group 2.
Safety & Procedures
Personal protective equipment should be worn at all times when handling methyl ethanoate to prevent contact with the skin, eyes, nose and throat. If contact is made with the skin, immediately wash the contaminated area and seek medical attention. If contact is made with the eyes, immediately wash with large amounts of water. If swallowed, seek medical attention immediately.
When opening containers or moving opened containers, they must be fully resealed and maintained in an upright position to prohibit leakages.
If methyl ethanoate is spilt, isolate the leak for at least 50 metres in all directions. In the event of a fire, water extinguishers may be ineffective due to methyl acetate’s low flashpoint. Foam extinguishers that are alcohol-resistant are suitable for small and large fires.
What is methyl ethanoate used for?
Industry Uses
Industry uses of methyl ethanoate involve the reaction of carbonylation to produce acetic anhydride. It is also used in paint and coating adhesives, lubricants, intermediates, processing aids and as a solvent in paint, glue, nail polish and graffiti removers.
Methyl ethanoate is also used as a chemical intermediate for the synthesis of chlorophacinone, diphacinone, fenfluramine, o-methoxyphenylacetone, p-methoxyphenylacetone, methyl cinnamate, methyl cyanoacetate, methyldopa, and phenylacetone and in the manufacturing of cellulose adhesives and perfumes.
Commercial Uses
Methyl ethanoate is used commercially as a flavouring agent in food additives for rum, brandy, whisky, in adhesives, cleaning products, personal care and cosmetic products, lubricants, fast-paced drying paints such as lacquers, motor vehicle coatings, furniture coatings, industrial coatings (low boiling point) inks, resins, oils artificial leathers and electronic products. The main user end markets for this product are the paint, coatings, cosmetic, textiles and motor industries.



